js 的操作
对数组的常用函数
map
对于所有元素执行相同操作
如 [1,2,3].map(p=>p+1) 可以得到 [2,3,4],这个 p 代指操作时的每一个元素,p=>p+1 本质上是个函数
再比如 dv.pages(`"目标文件夹"`).map(p=>p.file.tags) 得到目标文件夹下所有笔记的标签
filter
只保留返回为 true 的元素
如 dv.pages(`"目标文件夹"`).filter(p=>p.file.tags.includes('标签') 只保留了标签中含 标签 的那些文件数据
Array
其他的可以阅读下列链接
JavaScript 数组参考手册
字符串
dv 函数
dc.current()dv.page(path)dv.pagePaths(source)dv.pages(source)dv.header(level,values)dv.paragraph(values)dv.list(values)dv.table(headers, values)dv.taskList(tasks, groupByFile)
current()
获取当前页面文件的信息
page(path)
输入一个路径,获取目标文件的信息
pagePaths(source)
输入文件夹路径或标签,仅获取所有满足条件的文件的路径
pages(source)
输入文件夹路径或标签,获取所有满足条件的文件的信息
如:dv.pages(`"目录"`)(虽然我也不知道为啥要套两个引号)、dv.pages(`#标签`)(不过看样子正好对应了 dataview 的检索条件)
无论对于 current、page,还是 pages 的每一个元素,它们的信息都在 file 中
比如 dv.current().file.name、dv.pages(`"目录"`).filter(p=>p.file.folder=="目录")
file
对于这样的文件
| 子元素 | 含义 | 例如 |
|---|---|---|
| path | 路径 | 如:100-Index/test.md
|
| folder | 文件夹 | 如:100-Index
|
| name | 名字 | 如:test
|
| link | 和 name 一样的的链接 | (链接不好展示啊 |
| size | 大小(字节数) | 如:169
|
| ext | 后缀 | 如:md
|
| outlinks | 出链,也是链接类型 | |
| inlinks | 入链 | |
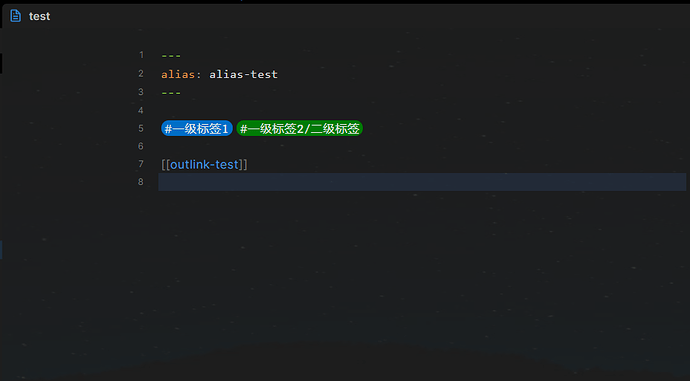
| etags | 标签 | ["#一级标签1", "#一级标签2/二级标签"] |
| tags | 标签 | ["#一级标签1", "#一级标签2/二级标签", "#一级标签2] |
| aliases | 别名 | 如:alias-test
|
| ctime | 创建时间 | |
| cday | 创建日期 | |
| mtime | 修改时间 | |
| mday | 修改日期 | 都是时间类型 |
| tasks | 所包含任务 | (感觉没啥用) |
header(level,values)
渲染一个标题,前面级别后面内容
paragraph(values)
渲染正文(反正除了表格,什么标题列表我都喜欢拿 paragraph 直接凑出来)
list(values)
输入一个数组,渲染出列表(不过我不晓得怎么渲染数字列表,一般我是拿 paragraph 渲染出的)
table(headers, values)
输入两个数组,前面的是一维数组-表头,后面的是二维数组-内容,一个数组为一行
```dataviewjs
dv.table(['a','b'],[['c','d'],['e','f']])
```
渲染的效果:
| a | b |
|---|---|
| c | d |
| e | f |
taskList(tasks, groupByFile)
渲染一个由page.file.tasks获得的Task对象的dataview任务列表。
第一个参数是必需的;如果提供第二个参数(须为真),那么将会按照文件的来源对任务列表进行分组。
关于yaml
yaml里的元素直接在page下面,而不在file中(与file并列)
如对于以下yaml
---
tags: a b c
date: 2022-04-14
abc: def
---
可以直接使用dv.page("目标文件").abc,dv.page("目标文件").tags来获取yaml中的元素
但是值得注意的一点是,.tags和.file.tags是有区别的
- 前者不做任何解析,单纯获取yaml中的内容,是字符串或数组类型(应该没人拿纯数字当标签吧
 )
) - 后者获取笔记中所有标签,是数组类型
关于时间处理
对于如上的.date,我觉得它应该是个字符串来着,但后来发现ob会解析成DateTime类型(当然直接渲染还是得到上述字符串)
无论是.file.cday等四个还是.date,我一般的做法是先转换成数字得到诸如1649865600000的数字(这是时间戳,是指格林威治时间自1970年1月1日(00:00:00 GMT)至当前时间的总秒数),然后再传入moment()处理
moment()可以解析字符串(2022-04-14或2022-04-14T10:20:90之类的),这样的字符串可以直接传入moment(),
关于momentjs的更多信息,可以点击下面的链接
- 文档 | Moment.js 中文网
- moment常用操作(日期加减、获取月初月末、季度、年)_Schafferyy的博客-CSDN博客_moment 月末
- momentjs 常用总结_嗯嗯好的就这样的博客-CSDN博客_diff moment 季度
dataview数组
dataviewjs返回的列表不是普通的javascript数组,而是具有额外功能的dataview数组,一般由可以返回多个结果的函数得到的,比如dv.pages(),也可以使用dv.array(array)明确地将一个普通的javascript数组转换成dataview数组。
接下来是dataview数组的完整接口,来自于datavie文档,感兴趣的读者可以自行研究
/** A function which maps an array element to some value. */
export type ArrayFunc<T, O> = (elem: T, index: number, arr: T[]) => O;
/** A function which compares two types (plus their indices, if relevant). */
export type ArrayComparator<T> = (a: T, b: T) => number;
/**
* Proxied interface which allows manipulating array-based data. All functions on a data array produce a NEW array
* (i.e., the arrays are immutable).
*/
export interface DataArray<T> {
/** The total number of elements in the array. */
length: number;
/** Filter the data array down to just elements which match the given predicate. */
where(predicate: ArrayFunc<T, boolean>): DataArray<T>;
/** Alias for 'where' for people who want array semantics. */
filter(predicate: ArrayFunc<T, boolean>): DataArray<T>;
/** Map elements in the data array by applying a function to each. */
map<U>(f: ArrayFunc<T, U>): DataArray<U>;
/** Map elements in the data array by applying a function to each, then flatten the results to produce a new array. */
flatMap<U>(f: ArrayFunc<T, U[]>): DataArray<U>;
/** Mutably change each value in the array, returning the same array which you can further chain off of. */
mutate(f: ArrayFunc<T, any>): DataArray<any>;
/** Limit the total number of entries in the array to the given value. */
limit(count: number): DataArray<T>;
/**
* Take a slice of the array. If `start` is undefined, it is assumed to be 0; if `end` is undefined, it is assumbed
* to be the end of the array.
*/
slice(start?: number, end?: number): DataArray<T>;
/** Concatenate the values in this data array with those of another data array. */
concat(other: DataArray<T>): DataArray<T>;
/** Return the first index of the given (optionally starting the search) */
indexOf(element: T, fromIndex?: number): number;
/** Return the first element that satisfies the given predicate. */
find(pred: ArrayFunc<T, boolean>): T | undefined;
/** Find the index of the first element that satisfies the given predicate. Returns -1 if nothing was found. */
findIndex(pred: ArrayFunc<T, boolean>): number;
/** Returns true if the array contains the given element, and false otherwise. */
includes(element: T): boolean;
/**
* Return a sorted array sorted by the given key; an optional comparator can be provided, which will
* be used to compare the keys in leiu of the default dataview comparator.
*/
sort<U>(key: ArrayFunc<T, U>, direction?: 'asc' | 'desc', comparator?: ArrayComparator<U>): DataArray<T>;
/**
* Return an array where elements are grouped by the given key; the resulting array will have objects of the form
* { key: <key value>, rows: DataArray }.
*/
groupBy<U>(key: ArrayFunc<T, U>, comparator?: ArrayComparator<U>): DataArray<{ key: U, rows: DataArray<T> }>;
/**
* Return distinct entries. If a key is provided, then rows with distinct keys are returned.
*/
distinct<U>(key?: ArrayFunc<T, U>, comparator?: ArrayComparator<U>): DataArray<T>;
/** Return true if the predicate is true for all values. */
every(f: ArrayFunc<T, boolean>): boolean;
/** Return true if the predicate is true for at least one value. */
some(f: ArrayFunc<T, boolean>): boolean;
/** Return true if the predicate is FALSE for all values. */
none(f: ArrayFunc<T, boolean>): boolean;
/** Return the first element in the data array. Returns undefined if the array is empty. */
first(): T;
/** Return the last element in the data array. Returns undefined if the array is empty. */
last(): T;
/** Map every element in this data array to the given key, and then flatten it.*/
to(key: string): DataArray<any>;
/**
* Recursively expand the given key, flattening a tree structure based on the key into a flat array. Useful for handling
* heirarchical data like tasks with 'subtasks'.
*/
expand(key: string): DataArray<any>;
/** Run a lambda on each element in the array. */
forEach(f: ArrayFunc<T, void>): void;
/** Convert this to a plain javascript array. */
array(): T[];
/** Allow iterating directly over the array. */
[Symbol.iterator](): Iterator<T>;
/** Map indexes to values. */
[index: number]: any;
/** Automatic flattening of fields. */
[field: string]: any;
}
最后
-
额,前几天立下 flag 说写篇文章介绍一下 Dataviewjs,今天终于来填坑了
 ,如果发现了什么错误请提醒我修改
,如果发现了什么错误请提醒我修改 -
所以说我之前的文章中的操作只不过是上述那些函数排列组合,什么map啊,filter啊,就是想办法提取出自己想要的数据,最后把数据按自己的喜好渲染出来
-
不过我也要提醒一下,如无必要,勿增需求,这些东西都是为了管理笔记而服务,到底有没有用,值不值得花费时间学来用,还得各位自行斟酌